Table of Contents

BNB Chain Governance refers to a collective decision-making system that oversees the on-chain operations and the implementation of changes within the network. This system ensures that decisions regarding upgrades, security, and community initiatives are made collectively and transparently.
Following the BC Fusion, BNB Chain will be making certain upgrades to its governance process. In this blog, we will explore the structure and processes behind BNB Chain’s Governance and discover how these changes enhance the network’s efficiency.
The Revamped BNB Chain’s On-Chain Governance
On-chain governance is a process where decisions are made and implemented on the blockchain. In the case of BNB Chain, proposals for upgrades and changes are submitted to the BNB Chain Governance. These on-chain governance proposals are established on Tally, with separations for both the mainnet and testnet.
Proposals can be submitted for a variety of reasons, including:
- System Upgrades: Introducing new features or improving existing ones.
- Bug Fixes: Addressing and resolving any technical issues or vulnerabilities.
- Policy Changes: Modifying governance rules or operational policies.
- Resource Allocation: Deciding on the distribution of funds or resources for development, marketing, or other purposes.
By leveraging on-chain governance, BNB Chain ensures that all decisions are transparent, verifiable, and subject to community approval.
Breaking Down the Proposal Process
The overall proposal process can be broken down into the following steps:
- Temperature check (on Snapshot)
- Formal Proposal (through Tally)
#1 Temperature Check
The governance process begins with a temperature check, which is usually conducted through the Snapshot platform. This phase allows any BNB holder to gauge community sentiment on a proposal.
If the proposal receives sufficient support during this phase, it moves to the final decision voting.
Steps involved:
- The Proposer submits their proposal.
- The community provides feedback on existing proposals.
- The Proposer incorporates the feedback. If the proposal has enough support, it moves to the next stage.
#2 Formal Proposal
In the final decision voting phase, on-chain voting takes place. This involves validators and those with staked BNB casting their votes to determine whether the proposal should be implemented or rejected. This phase of the governance process takes place in the Tally platform.
To vote on a live proposal, follow these steps. Here’s a detailed guide on how to vote on proposals:
Check your voting power
Ensure you have enough voting power to participate in the voting process. Your voting power is typically determined by the amount of governance tokens you hold.
You may delegate your voting power to a validator or choose to vote directly yourself.
Creating a proposal
If you have sufficient voting power, you can create proposals on the BSC network. To prevent spamming, a user can only have one active or pending proposal at a time.
When creating a proposal, you can add a title, description, and a list of actions.
A text proposal requires only a title and a description and will not be executed by the network as it does not include actions.
Voting on proposals
To vote on a proposal, click on the “Vote on chain” button. You will have three voting options:
- For: Support the proposal.
- Against: Oppose the proposal.
- Abstain: Neither support nor oppose the proposal.
Select your preferred option. Your vote will be recorded on the blockchain, contributing to the overall decision-making process.
Once the voting period is over, you can check if the proposal reached the quorum and the outcome of the vote.
What Are The Changes Being Made In The Governance Process?
The process explained above is the newly revamped BNB Chain governance process. The new process allows BNB stakers, not just validators, to participate in voting. Stakers can also delegate their voting power to others. Additionally, the temperature check procedure has been introduced to initiate discussions on governance issues before formal proposals are made.
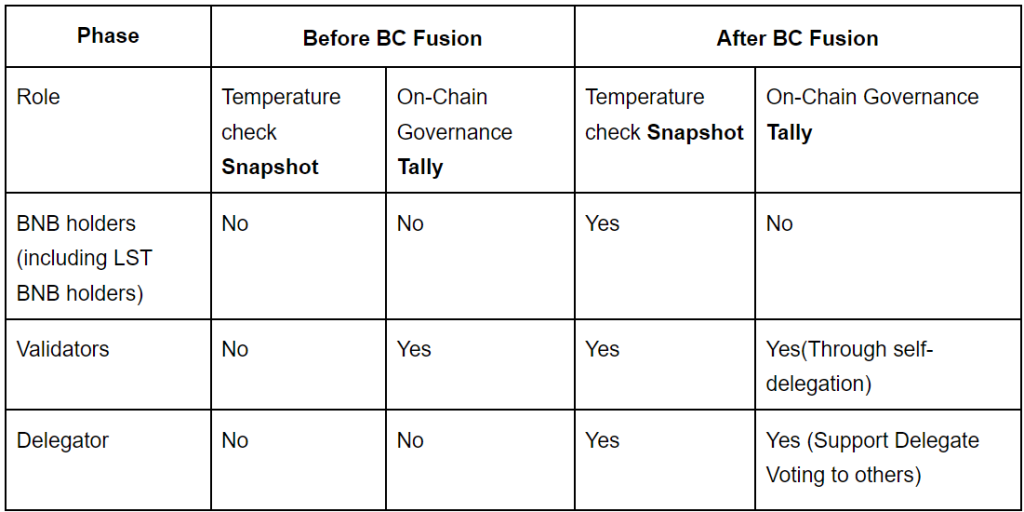
Here are the benefits of this revamped approach:
- Transparency: All decisions and their rationales are visible to the community, fostering an environment of openness.
- Adaptability: The governance system allows the network to respond quickly to technological and regulatory changes.
- Engagement: By enabling BNB stakers to participate directly in governance, the system encourages active community participation and a sense of ownership among stakeholders.
- Efficiency: Efficient governance optimizes resource allocation, ensuring that the network’s resources are used effectively to address the most critical issues and opportunities.
- Innovation: A robust governance framework promotes the introduction of new ideas and continuous improvements, driving innovation within the BNB Chain ecosystem.
Conclusion
By allowing validators and BNB stakers to participate directly in decision-making, the governance system enhances the network’s efficiency and security and also fosters a vibrant and engaged community. We believe that the revamped governance process will help build a more inclusive community for the BNB Chain ecosystem.


